Redshift RA3 Nodes and AQUA
Overview
AWS announced its new-generation redshift node types named RA3 which decouples the compute and storage enabling users to manage and scale independently based on needs.
The purpose of article to introduce RA3 node types and provide a comparison with existing node types. In the end I will also discuss about the migration options to RA3 nodes Let’s get started.
What is Redshift RA3?
RA3 nodes are built on the next generation Nitro powered compute instances which comes with high-bandwidth networking, managed storage that uses local SSD-based storage backed by Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3).
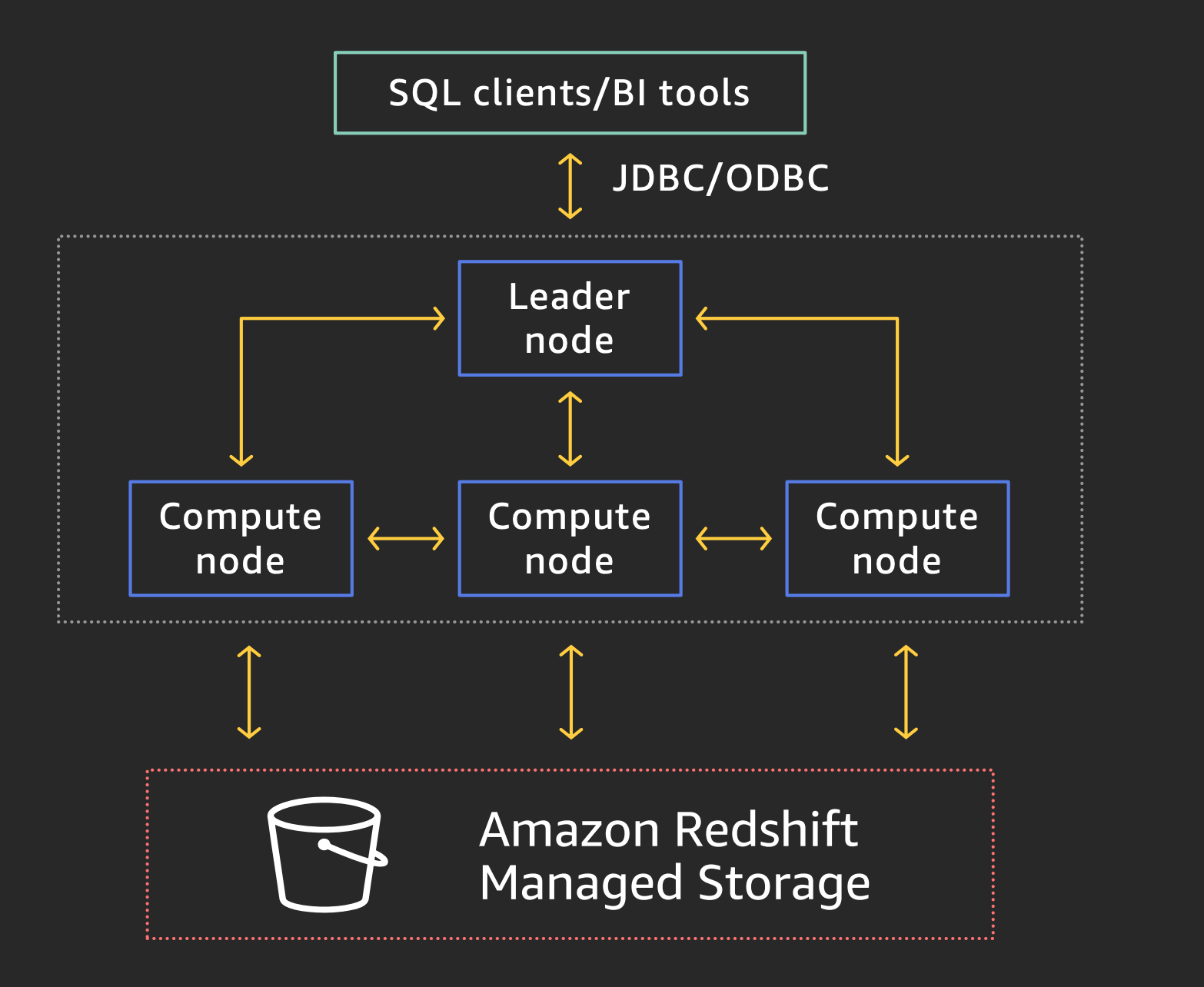 Redshift Managed Storage Architecture
Redshift Managed Storage Architecture
RA3 instances with managed storage use high performance SSDs for hot data and Amazon S3 for your cold data, providing ease of use, cost-effective storage, and high query performance.
How RA3 Works?
-
Permanent Redshift data is stored in S3
-
Local disk acts as a cache to hold ‘hot’ data
-
Data is retrieved from S3 on-demand using high bandwidth networking .(Thanks for Nitro based instances)
-
Data is removed from cluster local node using LRU method
-
Storage scales independently based on needs until the upper limit
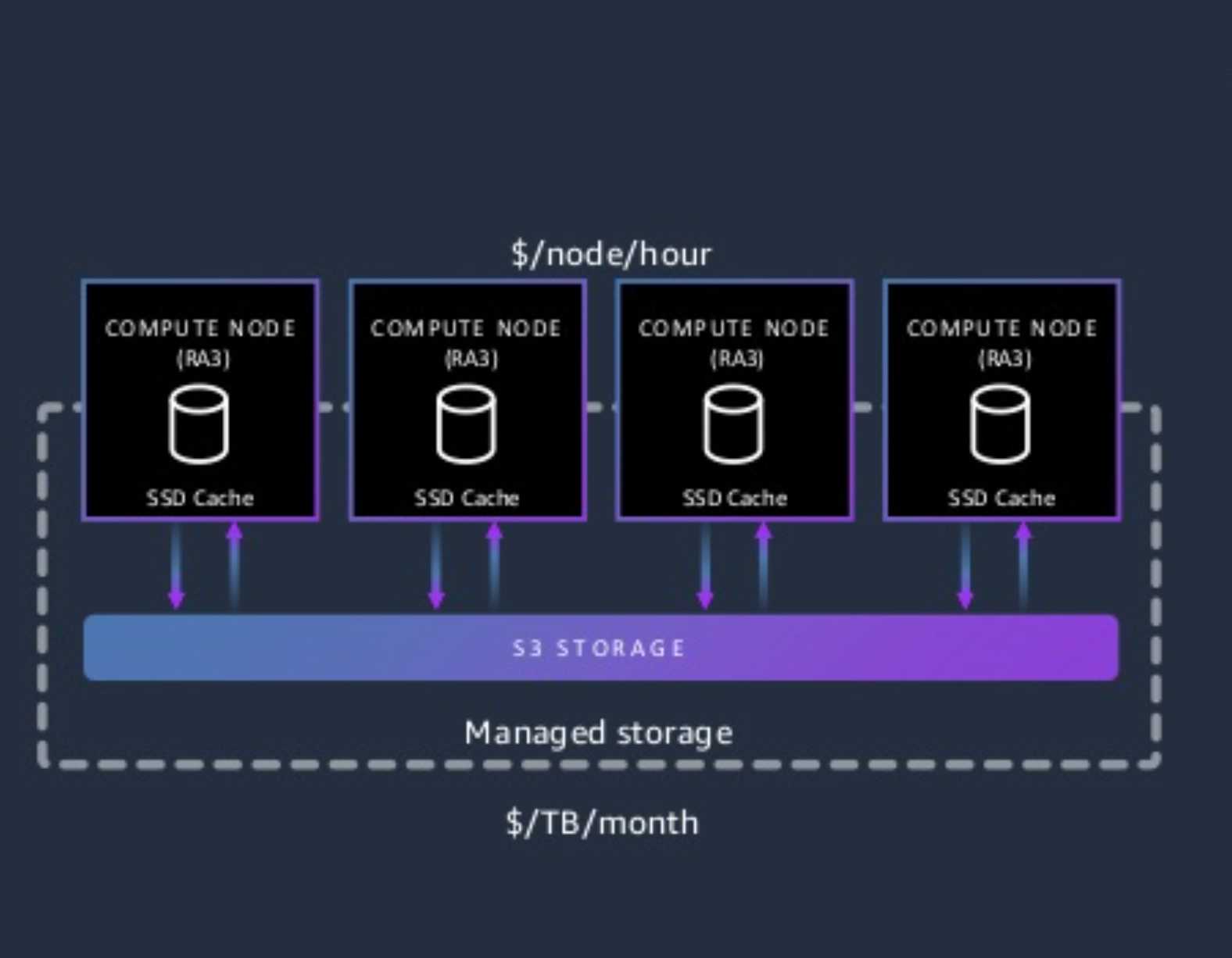 High Speed Cache and Networking in RA3
High Speed Cache and Networking in RA3
RA3 Node Options
-
RA3.4XL — 12 vCPU, 96 GiB Memory, 2 GB IO
-
RA3.16XL — 48 vCPU, 384 GiB Memory, 8 GB IO
Below table has the configuration of redshift nodes with slice count. Parallel execution of queries depends on number of slices.
A slice is nothing but a virtual compute node
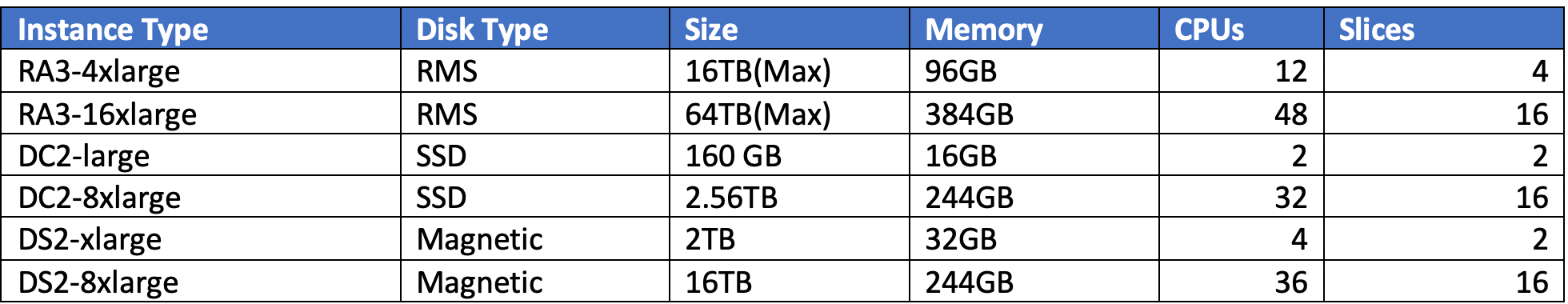 Redshift Node Configurations
Redshift Node Configurations
Cost Comparison between existing and RA3 Nodes:At first glance RA3 nodes seems more expensive but it can yield significant savings for users running lots of spectrum queries which charges for data scanned per query along with amazing performance benefits.
Up-to 2x performance and 2x storage capacity compared to DS2, 8x or more storage capacity compared to DC2
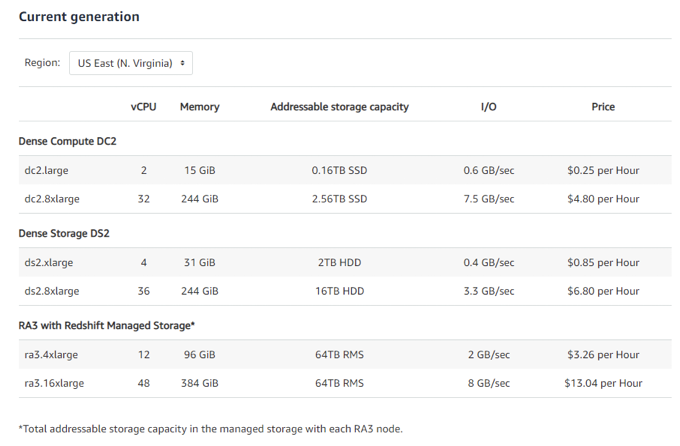 Redshift Node Comparison
Redshift Node Comparison
Note: RA3 Cluster needs minimum 2 Nodes
AQUA — Advanced query Accelerator
If you are not yet impressed by RA3’s managed storage,High bandwidth networking ,High speed cache and flexibility, there is one more thing to consider.-Its is AQUA and available for RA3 node type with no additional changes.
AQUA is a new distributed and hardware-accelerated cache for Amazon Redshift that delivers up to 10x better query performance than other cloud data warehouses.
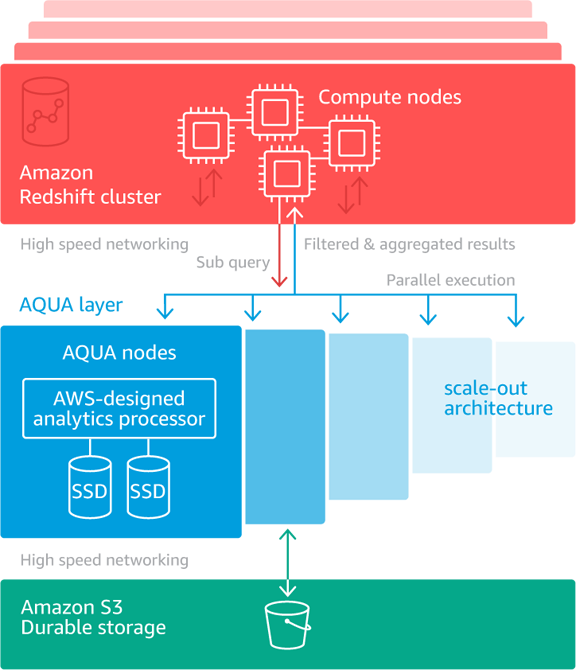
Image : https://aws.amazon.com/about-aws/whats-new/2020/12/aws-announces-aqua-for-amazon-redshift-preview/
Excited? Here are the options to migrate from existing node types to RA3.
Migration Options
To migrate your cluster from an existing node type to RA3, use one of the following methods:
-
Elastic resize: This is the most efficient way to change the instance type and update the nodes in your Amazon Redshift cluster. The cluster endpoint doesn’t change and the downtime during resize is minimal.
-
Snapshot and restore method: Choose the snapshot and restore method if elastic resize is unavailable (from a mismatch between slice and node count). This method minimizes the amount of time for production writes.
-
Classic resize: Choose the classic resize method if it’s the only option available. For single node clusters, only a classic resize can be performed to convert the cluster into a multi-node cluster.
Summary
RA3 node types works best for below use-cases.
-
You need the flexibility to scale and pay for compute separate from storage
-
You query a fraction of your total data.
-
Your data volume is growing rapidly or is expected to grow rapidly.
-
You want the flexibility to size the cluster based only on your performance needs.
References
Amazon Redshift RA3 - Amazon Web Services Scale compute and storage independently for fast query performance and lower costs As the scale of data continues to…aws.amazon.com Amazon Redshift clusters In the following sections, you can learn the basics of creating a data warehouse by launching a set of compute nodes…docs.aws.amazon.com
https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/redshift-ra3-node-type/